Emotion and Logic, Fast and Slow: Decoding Decision-Making Approaches of 4 Distinct Personalities! 🧩


Ever wondered why some folks jump headfirst into decisions while others meticulously weigh every option? It's like trying to decode the unique personalities behind our choices. Well, that's precisely what we're diving into today. You see, there are these four intriguing categories of decision-makers that go way beyond just buying stuff. They're like the friends we all have - the 'Let's do it now,' the 'Show me the numbers,' the 'I need details,' and the 'Tell me a story' types. And believe it or not, these categories aren't just about shopping; they're about how we all approach decisions in life. I've even found myself associating each category with someone I know - the friend who always says 'Let's go for it,' the data-driven colleague, the meticulous planner, and the one who seeks stories in everything.
The Concept
Brian and Jeffrey Eisenberg, well-known for their work in the field of digital marketing and optimization, have discussed buyer modalities in terms of emotions and logic, as well as fast and slow thinking processes. They often discuss these concepts in the context of understanding consumer behavior and decision-making.
Four Buyer Modalities
The Eisenbergs propose that there are four primary buyer modalities, which can be described as follows:
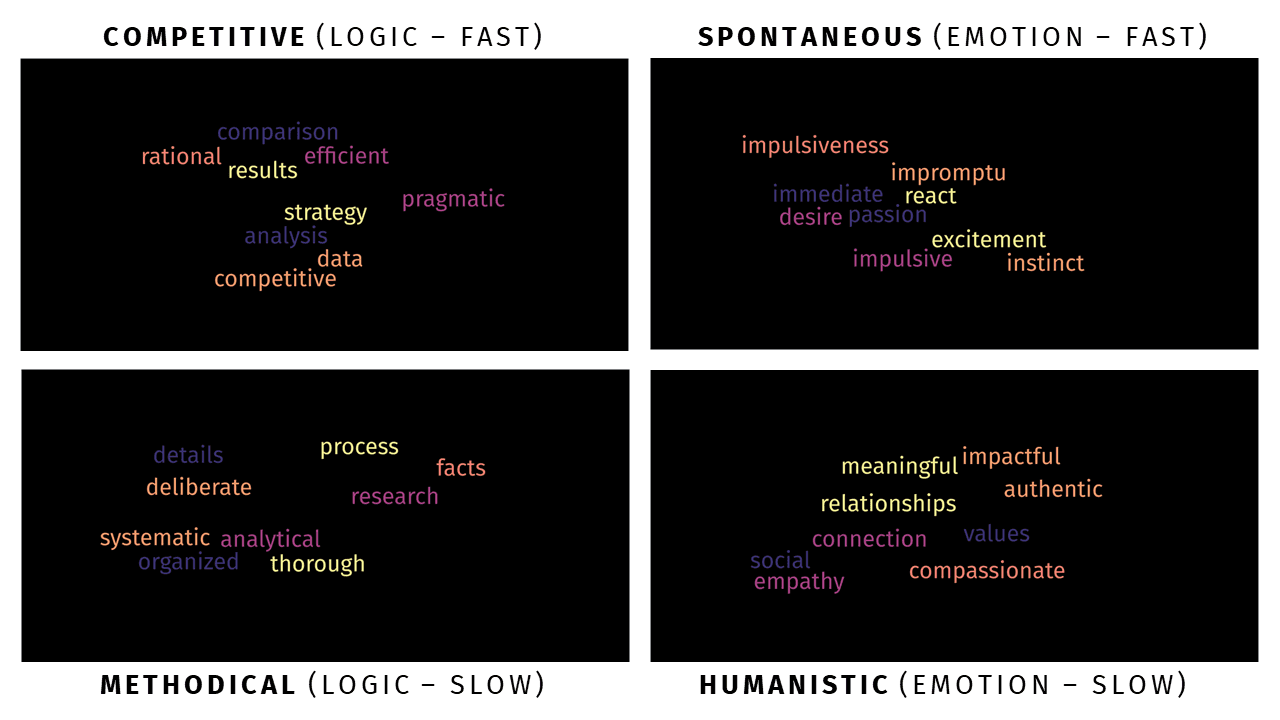
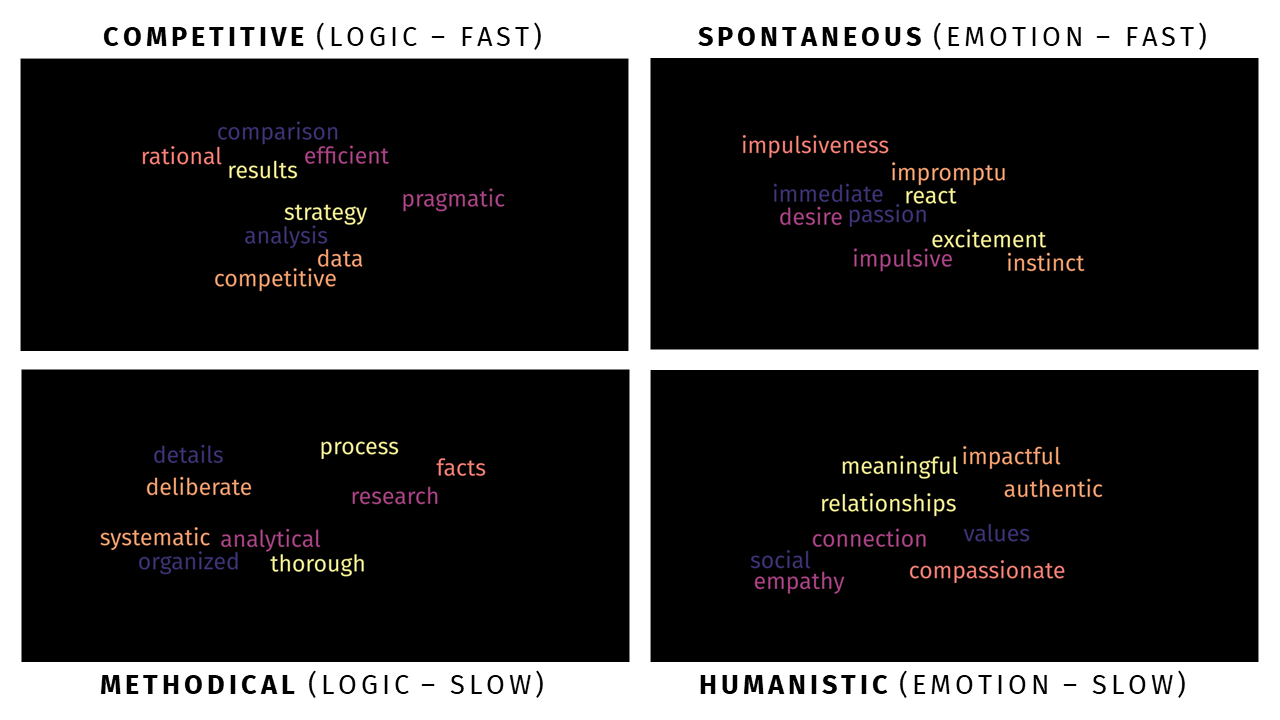
1. Competitive (Logic - Fast)
Competitive buyers are motivated by logic and fast thinking. They focus on facts, figures, and practical benefits when making purchasing decisions. They want to know how a product or service will solve their problems and provide tangible benefits.
2. Spontaneous (Emotion - Fast)
Spontaneous buyers are driven by emotion and fast thinking. They make decisions based on immediate emotional reactions and are drawn to products or services that evoke strong feelings or desires.
3. Methodical (Logic - Slow)
Methodical buyers are motivated by logic and slow thinking. They take their time to research and evaluate options, looking for detailed information and a clear rationale before making a decision.
4. Humanistic (Emotion - Slow)
Humanistic buyers are driven by emotion and slow thinking. They seek deep connections with brands and products, valuing the emotional aspects of their purchases and often focusing on the social and personal impact of their decisions.
Takeaway
Understanding these buyer modalities can help businesses tailor their marketing messages and strategies to effectively reach and engage with different types of consumers. It acknowledges that not all consumers make decisions in the same way, and successful marketing often involves appealing to both emotional and logical aspects of the buying process, as well as accommodating different decision-making speeds.
Contrarian View
Some critics argue that categorizing individuals into distinct decision-making modalities, such as the four presented by the Eisenbergs, oversimplifies the intricate nature of human choices. They contend that human decision-making is influenced by a multitude of factors, including individual differences and the specific context, making it challenging to neatly fit people into predefined categories.
Alternative Approaches
1. VALS (Values, Attitudes, and Lifestyle)
VALS is a psychographic system that segments individuals based on their values, attitudes, and lifestyles, resulting in distinct consumer segments.
2. Personality-Based Typologies
VALS is a psychographic system that segments individuals based on their values, attitudes, and lifestyles, resulting in distinct consumer segments.
3. Segmentation Based on Needs and Goals
Consumers are categorized based on their primary motivations, such as price sensitivity, quality-consciousness, or convenience-driven preferences.
These alternative approaches offer varying perspectives on understanding decision-making behavior, recognizing the diversity and complexity of human choices.