Expression and Empathy: Navigating Plutchik's Wheel of Emotions - Pairs, Combinations, and Intensities! 🧩

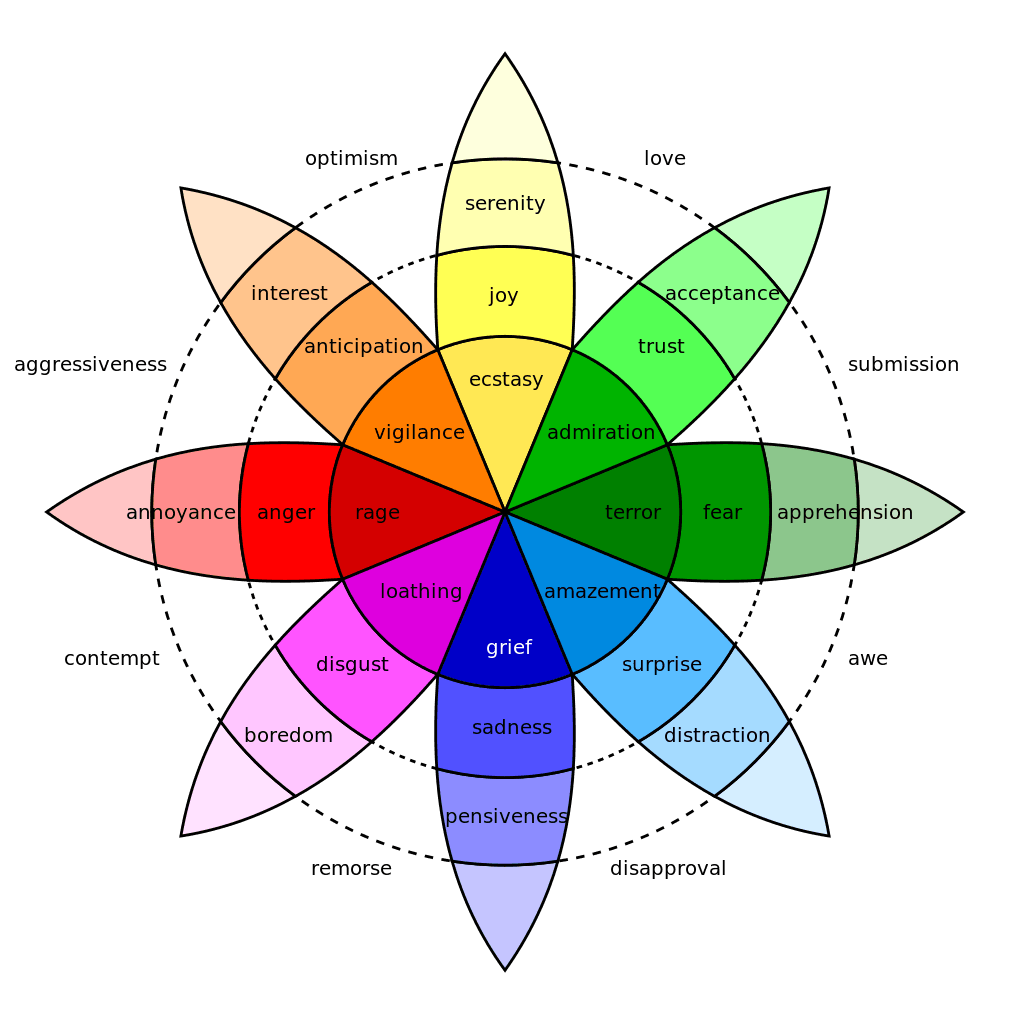

Emotions can be complex, but Plutchik's Wheel of Emotions simplifies the journey. It helps us grasp the depth of feelings, from subtle to intense. Expression is about sharing what's inside, while empathy lets us feel what others go through, forming the heart of human connection. In this exploration, we'll summarize the emotional pairs, intensities, and combinations that shape our lives, all through the lens of Plutchik's model.
Primary Emotion Pairs
At the core of Plutchik's Wheel lie eight primary emotions, grouped into four complementary pairs. These pairs signify the duality of our emotional responses:
| Emotion Pair | Emotion | Opposite Emotion |
|---|---|---|
| Joy vs. Sadness | Joy | Sadness |
| Trust vs. Disgust | Trust | Disgust |
| Fear vs. Anger | Fear | Anger |
| Surprise vs. Anticipation | Surprise | Anticipation |
These primary feelings serve as the bedrock of our emotional experiences, each varying in intensity and sometimes blending to form complex secondary and tertiary emotions. Recognizing and understanding these pairs can provide valuable insights into human behavior, decision-making, and interpersonal relationships.
Combined Emotions
Within Plutchik's framework, when two primary emotions merge, they give birth to a more nuanced feeling.
| Primary Emotions | Combined Emotion |
|---|---|
| Joy + Trust | Love |
| Trust + Fear | Submission |
| Fear + Surprise | Awe |
| Surprise + Sadness | Disapproval |
| Sadness + Disgust | Remorse |
| Disgust + Anger | Contempt |
| Anger + Anticipation | Aggressiveness |
| Anticipation + Joy | Optimism |
These combinations give insight into the complex interplay of emotions we experience. By understanding the primary emotions and their possible combinations, we gain a more profound sense of our emotional landscape.
Emotion Intensity Spectrum
Emotions aren't static; they fluctuate in strength and depth. Plutchik's Wheel of Emotions offers a lens to view these gradations, illustrating how our feelings intensify or soften based on our experiences.
| Emotion Pair | High Intensity | Medium Intensity | Low Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Joy vs. Sadness | Ecstasy | Joy | Serenity |
| Grief | Sadness | Pensiveness | |
| Trust vs. Disgust | Admiration | Trust | Acceptance |
| Loathing | Disgust | Boredom | |
| Fear vs. Anger | Terror | Fear | Apprehension |
| Rage | Anger | Annoyance | |
| Surprise vs. Anticipation | Amazement | Surprise | Distraction |
| Vigilance | Anticipation | Interest |
Understanding the spectrum is more than an academic exercise; it's a pathway to self-awareness. By grasping these variations, we can better articulate our feelings, empathize with others, and navigate the vast ocean of human emotion with greater clarity.
Contrarian Views
-
Simplicity vs. Complexity: Critics argue that the model oversimplifies the intricate nature of human emotions.
-
Lack of Cultural Specificity: Some believe the model may not be universally applicable, as emotions can vary significantly across cultures.
-
Limited Scientific Validation: Questions arise about the model's empirical validity and whether it has been rigorously tested.
-
Neglect of Cognitive Factors: The model primarily focuses on emotions, overlooking the role of cognitive appraisal.
-
Fluid Nature of Emotions: Critics argue that emotions are dynamic and can change rapidly, challenging fixed categories.
Reference
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Robert_Plutchik
Useful content for further reading
https://www.6seconds.org/2022/03/13/plutchik-wheel-emotions/